Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yoshida, Kenta*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Inoue, Koji*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*; Shimodaira, Masaki
Materia, 62(3), p.154 - 158, 2023/03
no abstracts in English
Hironaka, Kota; Ito, Fumiaki*; Lee, J.; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Takahashi, Tone; Suzuki, Satoshi*; Yogo, Akifumi*; Arikawa, Yasunobu*; Abe, Yuki*
Dai-42-Kai Nihon Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai Nenji Taikai Kaigi Rombunshu (Internet), 4 Pages, 2021/11
Neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) is a method for non-destructive measurement of nuclear material by using a time-of-flight (TOF) technique with a pulsed neutron source. For NRTA system to carry out the short-distance TOF measurements with high resolutions, a short-pulsed neutron source is required. Laser-driven neutron sources (LDNSs) is very suitable as such a neutron source because of its short pulse width. Moreover, the compactness of the laser system is also expected due to the remarkable development of laser technology in recent years. In the present study, we have developed a technology for applying LDNS to the NRTA system and conducted the demonstration experiment using the LFEX laser at Osaka University to investigate the feasibility of the system. In this experiment, we successfully observed the neutron resonance peaks of indium and silver samples.
Toh, Yosuke; Ozu, Akira; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kitatani, Fumito; Komeda, Masao; Maeda, Makoto; Koizumi, Mitsuo
Proceedings of INMM & ESARDA Joint Virtual Annual Meeting (Internet), 8 Pages, 2021/08
 Pd and
Pd and  Tc
TcToh, Yosuke; Segawa, Mariko; Maeda, Makoto; Tsuneyama, Masayuki*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Ebihara, Mitsuru*
Analytical Chemistry, 93(28), p.9771 - 9777, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:24.69(Chemistry, Analytical)Igarashi, Takahiro; Otani, Kyohei; Kato, Chiaki; Sakairi, Masatoshi*; Togashi, Yusuke*; Baba, Kazuhiko*; Takagi, Shusaku*
ISIJ International, 61(4), p.1085 - 1090, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:8.06(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)In order to clarify the effect of metal cations (Zn , Mg
, Mg , Na
, Na ) in aqueous solution on hydrogen permeation into iron, the amount of hydrogen permeation from iron surface was measured by electrochemical tests with a laser ablation. Moreover, in order to obtain the basic mechanism of hydrogen permeation with metal cation, first-principles calculations were used to acquire the adsorption potential of the metal cation and the electronic state around iron surface. By Zn
) in aqueous solution on hydrogen permeation into iron, the amount of hydrogen permeation from iron surface was measured by electrochemical tests with a laser ablation. Moreover, in order to obtain the basic mechanism of hydrogen permeation with metal cation, first-principles calculations were used to acquire the adsorption potential of the metal cation and the electronic state around iron surface. By Zn in solution, anodic reaction on ablated surface by laser irradiation was suppressed. Also, by quantum analysis Zn atoms were chemically bonded stronger than Na and Mg atoms to iron surface. It was suggested that the dissolution reaction of iron was suppressed by the formation of the Zn layer, and that lead suppression of hydrogen permeation into iron.
in solution, anodic reaction on ablated surface by laser irradiation was suppressed. Also, by quantum analysis Zn atoms were chemically bonded stronger than Na and Mg atoms to iron surface. It was suggested that the dissolution reaction of iron was suppressed by the formation of the Zn layer, and that lead suppression of hydrogen permeation into iron.
Ogawa, Shuichi*; Yamaguchi, Hisato*; Holby, E. F.*; Yamada, Takatoshi*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Takakuwa, Yuji*
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 11(21), p.9159 - 9164, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:18.31(Chemistry, Physical)Atomically thin layers of graphene have been proposed to protect surfaces through the direct blocking of corrosion reactants such as oxygen with low added weight. The long term efficacy of such an approach, however, is unclear due to the long-term desired protection of decades and the presence of defects in as-synthesized materials. Here, we demonstrate catalytic permeation of oxygen molecules through previously-described impermeable graphene by imparting sub-eV kinetic energy to molecules. These molecules represent a small fraction of a thermal distribution thus this exposure serves as an accelerated stress test for understanding decades-long exposures. The permeation rate of the energized molecules increased 2 orders of magnitude compared to their non-energized counterpart. Graphene maintained its relative impermeability to non-energized oxygen molecules even after the permeation of energized molecules indicating that the process is non-destructive and a fundamental property of the exposed material.
Toh, Yosuke
JAEA-Conf 2019-001, p.47 - 52, 2019/11
no abstracts in English
Toh, Yosuke; Ozu, Akira; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kitatani, Fumito; Komeda, Masao; Maeda, Makoto; Koizumi, Mitsuo
Proceedings of INMM 60th Annual Meeting (Internet), 7 Pages, 2019/07
Toh, Yosuke; Ozu, Akira; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kitatani, Fumito; Komeda, Masao; Maeda, Makoto; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Heyse, J.*; Paradela, C.*; et al.
Proceedings of INMM 59th Annual Meeting (Internet), 9 Pages, 2018/07
Toh, Yosuke; Ozu, Akira; Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kitatani, Fumito; Komeda, Masao; Maeda, Makoto; Kureta, Masatoshi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Seya, Michio; et al.
EUR-28795-EN (Internet), p.684 - 693, 2017/00
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Kitatani, Fumito; Maeda, Makoto; Kureta, Masatoshi
Proceedings of INMM 57th Annual Meeting (Internet), 6 Pages, 2016/07
From a viewpoint of nuclear safeguards and nuclear security, it has recently become important to develop a non-destructive assay (NDA) system that accurately determines the amount of special nuclear materials (SNMs) in various samples such as spent fuels, next generation MA-Pu fuels and fuel debris. One candidate of those NDA techniques is neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA). It relies on a neutron time-of-flight measurement and is a well-established method to apply for the accurate evaluations of nuclear data, including total cross sections and resonance parameters. The potential of NRTA to quantify SNM in complex materials has been already demonstrated by performing NRTA measurement at IRMM/GELINA under collaboration of JAEA and JRC. However, a present NRTA system usually has a large electron accelerator facility to generate intense neutrons, whereas this is very difficult to apply to various facilities that need to measure SNM. Therefore a compact NRTA system would be required for practical applications of quantifying SNM in a variety of samples. In order to realize a compact NRTA system, we are developing a prototype with a D-T neutron generator that has a pulse width of 10  s and an average maximum neutron yield ranging from
s and an average maximum neutron yield ranging from 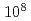 n/s to
n/s to 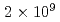 n/s. Numerical calculations were used to optimize the system performance to quantify SNM and MA in spent and MA-Pu fuels. In this presentation, those numerical calculation results, together with a brief description of the prototype, are presented. In addition, we discuss a future prospect of a compact NRTA system equipped with a neutron source with a shorter pulse width (ex. 100 ns) and a more intense neutron yield.
n/s. Numerical calculations were used to optimize the system performance to quantify SNM and MA in spent and MA-Pu fuels. In this presentation, those numerical calculation results, together with a brief description of the prototype, are presented. In addition, we discuss a future prospect of a compact NRTA system equipped with a neutron source with a shorter pulse width (ex. 100 ns) and a more intense neutron yield.
 -martensite as an intermediate phase during the strain-induced transformation of SUS304 stainless steel
-martensite as an intermediate phase during the strain-induced transformation of SUS304 stainless steelHatano, Masaharu*; Kubota, Yoshiki*; Shobu, Takahisa; Mori, Shigeo*
Philosophical Magazine Letters, 96(6), p.220 - 227, 2016/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:35.46(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We have investigated the formation process of  '-martensite from the
'-martensite from the  -phase induced by external strain using
-phase induced by external strain using  synchrotron diffraction experiments, combined with Lorentz transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and high-resolution TEM observations. It is clearly demonstrated that
synchrotron diffraction experiments, combined with Lorentz transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and high-resolution TEM observations. It is clearly demonstrated that  -martensite with hexagonal symmetry appears as an intermediate structure during the plastic deformation of SUS304 stainless steel. In addition to stacking faults and dislocations, interfaces between the twin structures presumably play a key role in the formation of
-martensite with hexagonal symmetry appears as an intermediate structure during the plastic deformation of SUS304 stainless steel. In addition to stacking faults and dislocations, interfaces between the twin structures presumably play a key role in the formation of  -martensite.
-martensite.
Oya, Yasuhisa*; Li, X.*; Sato, Misaki*; Yuyama, Kenta*; Oyaizu, Makoto; Hayashi, Takumi; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Okuno, Kenji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(3), p.402 - 405, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:68.36(Nuclear Science & Technology)The deuterium (D) permeation behaviors for ion damaged tungsten (W) by 3 keV D
 and 10 keV C
and 10 keV C were studied. The D permeability was obtained for un-damaged W at various temperatures. For both D
were studied. The D permeability was obtained for un-damaged W at various temperatures. For both D
 and C
and C implanted W, the permeability was clearly reduced. But, for the D
implanted W, the permeability was clearly reduced. But, for the D
 implanted W, the permeability was recovered by heating at 1173 K and it was almost consistent with that for un-damaged W. In the case of C
implanted W, the permeability was recovered by heating at 1173 K and it was almost consistent with that for un-damaged W. In the case of C implanted W, the permeability was not recovered even if the sample was heated at 1173 K, indicating that the existence of carbon would prevent the recovery of permeation path in W. In addition, TEM observation showed the voids were grown by heating at 1173 K and not removed, showing the existence of damages would not largely influence on the hydrogen permeation behavior in W in the present study.
implanted W, the permeability was not recovered even if the sample was heated at 1173 K, indicating that the existence of carbon would prevent the recovery of permeation path in W. In addition, TEM observation showed the voids were grown by heating at 1173 K and not removed, showing the existence of damages would not largely influence on the hydrogen permeation behavior in W in the present study.
Taguchi, Tomitsugu; Yamamoto, Shunya; Kodama, Katsuaki; Asaoka, Hidehito
Carbon, 95, p.279 - 285, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:35.58(Chemistry, Physical)Amorphous SiC nanotubes are successfully synthesized by 340 keV Si ions irradiation of polycrystalline SiC nanotubes for the first time. A polycrystalline/amorphous heterostructure SiC nanotube, in which polycrystalline SiC and amorphous SiC coexist in the same nanotube, is also synthesized by ions irradiation with a mask in front of polycrystalline SiC nanotube. According to electron energy loss spectroscopy evaluation, the plasmon energies of SiC nanotube change rapidly at the interface between polycrystalline and amorphous regions. The volume swelling by amorphization evaluated from the differences of plasmon energies is approximately 5.0%. This result reveals that the further relaxed amorphous SiC nanotubes with higher density can be produced. The graphitic shells in carbon layer of C-SiC nanotube gradually bend to the radial direction of nanotube by the ion irradiation. Since the graphite (002) spots in the selected area electron diffraction pattern are clearly observed even after the ion irradiation, the carbon layer in C-SiC nanotube has certain crystallinity. Moreover, the new multi-walled carbon nanotube with the graphitic shells completely parallel to the radial direction of nanotube is also produced inside the amorphous SiC tubular layer in the case of C-SiC nanotube with large caliber.
ions irradiation of polycrystalline SiC nanotubes for the first time. A polycrystalline/amorphous heterostructure SiC nanotube, in which polycrystalline SiC and amorphous SiC coexist in the same nanotube, is also synthesized by ions irradiation with a mask in front of polycrystalline SiC nanotube. According to electron energy loss spectroscopy evaluation, the plasmon energies of SiC nanotube change rapidly at the interface between polycrystalline and amorphous regions. The volume swelling by amorphization evaluated from the differences of plasmon energies is approximately 5.0%. This result reveals that the further relaxed amorphous SiC nanotubes with higher density can be produced. The graphitic shells in carbon layer of C-SiC nanotube gradually bend to the radial direction of nanotube by the ion irradiation. Since the graphite (002) spots in the selected area electron diffraction pattern are clearly observed even after the ion irradiation, the carbon layer in C-SiC nanotube has certain crystallinity. Moreover, the new multi-walled carbon nanotube with the graphitic shells completely parallel to the radial direction of nanotube is also produced inside the amorphous SiC tubular layer in the case of C-SiC nanotube with large caliber.
Seya, Michio; Naoi, Yosuke; Kobayashi, Naoki; Nakamura, Takahisa; Hajima, Ryoichi; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Kureta, Masatoshi; Nakamura, Hironobu; Harada, Hideo
Kaku Busshitsu Kanri Gakkai (INMM) Nihon Shibu Dai-35-Kai Nenji Taikai Rombunshu (Internet), 9 Pages, 2015/01
The Integrated Support Center for Nuclear Non-proliferation and Nuclear Security (ISCN) of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting (based on collaborations with JAEA other centers) the following basic technology development programs of advanced non-destructive detection/measurement of nuclear material for nuclear security and nuclear non-proliferation. (1) The demonstration test of the Pu-NDA system for spent fuel assembly using PNAR and SINRD (JAEA/USDOE(LANL) collaboration, completed in JFY2013), (2) Basic development of NDA technologies using laser Compton scattered  -rays (Demonstration of an intense mono-energetic
-rays (Demonstration of an intense mono-energetic  -ray source), (3) Development of alternative to He-3 neutron detection technology, (4) Development of neutron resonance densitometry (JAEA/JRC collaboration)This paper introduces above programs.
-ray source), (3) Development of alternative to He-3 neutron detection technology, (4) Development of neutron resonance densitometry (JAEA/JRC collaboration)This paper introduces above programs.
Tsuchiya, Harufumi; Harada, Hideo; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Kitatani, Fumito; Takamine, Jun; Kureta, Masatoshi; Iimura, Hideki; Kimura, Atsushi; Becker, B.*; Kopecky, S.*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 767, p.364 - 371, 2014/12
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:60.98(Instruments & Instrumentation)The impact of systematic effects on the areal density derived from a neutron resonance transmission analysis (NRTA) is investigated by measurements at the time-of-flight facility GELINA. The experiments were carried out at a 25 m station using metallic natural Cu discs with different thicknesses. To derive the areal density from a fit to the experimental transmission, the resonance shape analysis code REFIT was used. Large bias effects were observed using recommended resonance parameters. Therefore, neutron resonance parameters, in particular resonance energies and neutron widths, were derived from the transmission data obtained with a 0.25 mm thick Cu metallic sample. These parameters were used to study the impact of the resonance strength and sample thickness, on the accuracy of the areal density derived by NRTA.
Fukuoka, Osamu*; Matsunami, Noriaki*; Tazawa, Masato*; Shimura, Tetsuo*; Sataka, Masao; Sugai, Hiroyuki; Okayasu, Satoru
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 250(1-2), p.295 - 299, 2006/09
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:83(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have investigated the effects on electrical and optical properties of Al-doped ZnO (AZO) semiconductor films induced by high-energy heavy ion. The AZO films with c-axis on SiO glass substrate were prepared by a RF-sputter-deposition method at 400
glass substrate were prepared by a RF-sputter-deposition method at 400  C. Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy shows that the Al/Zn composition and the film thickness are 4 % and 0.3
C. Rutherford backscattering spectroscopy shows that the Al/Zn composition and the film thickness are 4 % and 0.3  m. No appreciable change was observed in optical transparency. We find that the conductivity monotonically increases from 1.5
m. No appreciable change was observed in optical transparency. We find that the conductivity monotonically increases from 1.5 10
10 to 8
to 8 10
10 S/cm with increasing the fluence up to 4
S/cm with increasing the fluence up to 4 10
10 /cm
/cm , as already been observed for 100 keV Ne irradiation. The fluence of 100 keV Ne at which the conductivity takes its maximum is 3
, as already been observed for 100 keV Ne irradiation. The fluence of 100 keV Ne at which the conductivity takes its maximum is 3 10
10 /cm
/cm (7 dpa). The dpa of 100 MeV Xe at 4
(7 dpa). The dpa of 100 MeV Xe at 4 10
10 /cm
/cm is estimated as 0.008. Hence, the conductivity increase by 100 MeV Xe ion is ascribed to the electronic excitation effects.
is estimated as 0.008. Hence, the conductivity increase by 100 MeV Xe ion is ascribed to the electronic excitation effects.
Iwai, Yasunori; Yamanishi, Toshihiko; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Nishi, Masataka; Yagi, Toshiaki; Tamada, Masao
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(1-7), p.815 - 820, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:70.56(Nuclear Science & Technology)Solid-polymer-electrolyte (SPE) water electrolysis is attractive in electrolytic process of water detritiation system (WDS) in fusion reactors because it can electrolyze liquid waste directly, but radioactive durability of its ion exchange membrane is a key point. Radioactive durability of Nafion, a typical commercial ion exchange membrane, was experimentally investigated using Co-60 irradiation facility and electron beam irradiation facility at Takasaki Radiation Chemistry Research Establishment of JAERI. Nafion is composed of PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) main chain. However the degradation of its mechanical strength by irradiation was significantly distinguished from that of PTFE and no serious damage was observed for its ion exchange capacity up to 530 kGy, the requirement of ITER. Atmospheric effects such as soaking and oxygen on degrading behaviors were discussed from the viewpoint of radical reaction mechanism. Dependencies of operating temperature and radioactive source are also demonstrated in detail.
Nakamura, Hirofumi; Sakurai, Shinji; Suzuki, Satoshi; Hayashi, Takumi; Enoeda, Mikio; Tobita, Kenji; DEMO Plant Design Team
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1339 - 1345, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:51 Percentile:94.78(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Ohira, Shigeru; Luo, G.; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Shu, Wataru; Kitamura, Kazunori*; Nishi, Masataka
Fusion Science and Technology, 48(1), p.621 - 624, 2005/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new conceptual design of a tritium permeation test module assembly was developed for demonstration tests using a strong plasma source constructed in TPL for simulation of practical tritium permeation in the real plasma facing components and validation of the models and codes for evaluation of tritium permeation. The target module, to be irradiated by the high flux plasma beam, consists of a multi-layer structure of a plasma facing material plate and a copper substrate with pressurized coolant cavity. Tests using a preliminary model of the target module has been performed to verify thermal and mechanical behavior of the bonded structure and to assess its structural integrity focused on the bonded interface under the cyclic heat loads. After the heat load testing, no visible defect and crack was observed around the bonded interfaces with magnifying glass, and its structural integrity was verified. Also the first tests using tritium plasma at TSTA/LANL with the preliminary model was performed and process to measured tritium permeated was established.